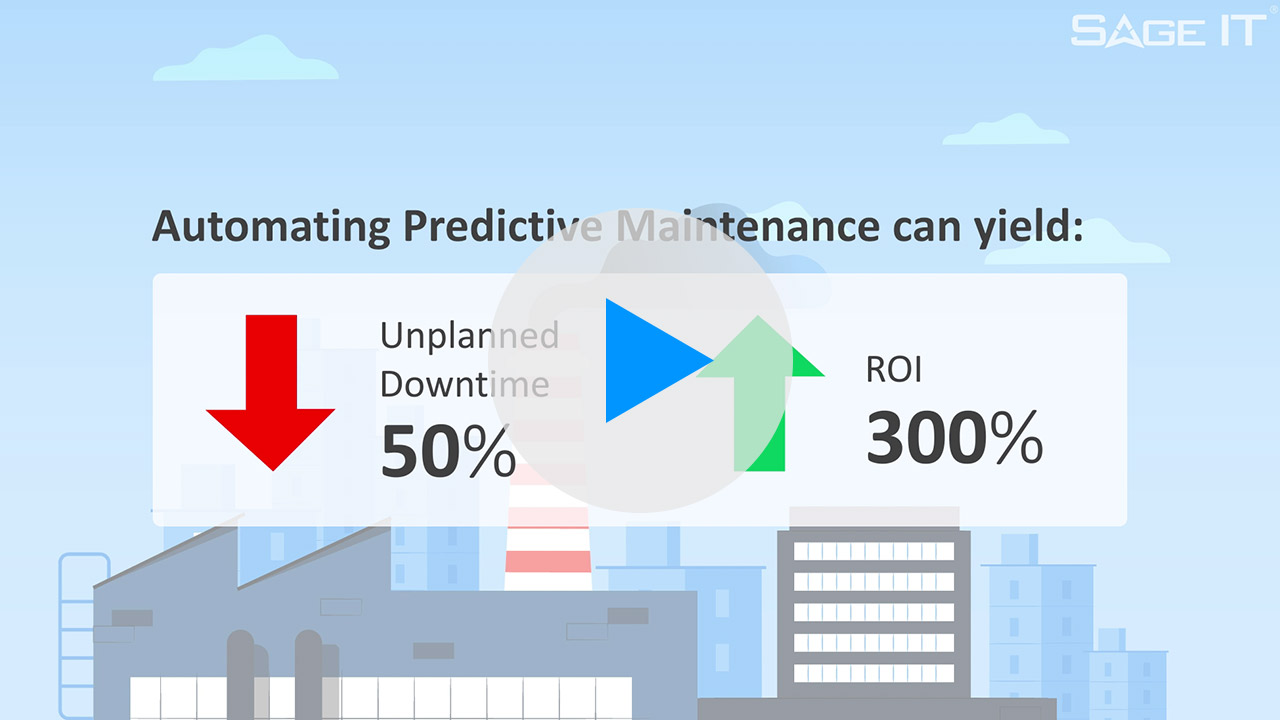
1. Identify target machine – RPA is used to review records to determine days’ list of machines that need PM work
2. Distribute work – based on availability and workload, RPA sends each tech a list of PMs that need to be completed. The list contains any special equipment needed for each job. Any high-priority PMs are identified.
3. [steps from 1.2 are executed]
4. Need part – at the end of the PM, a part is identified as being out of spec and needs replacement.
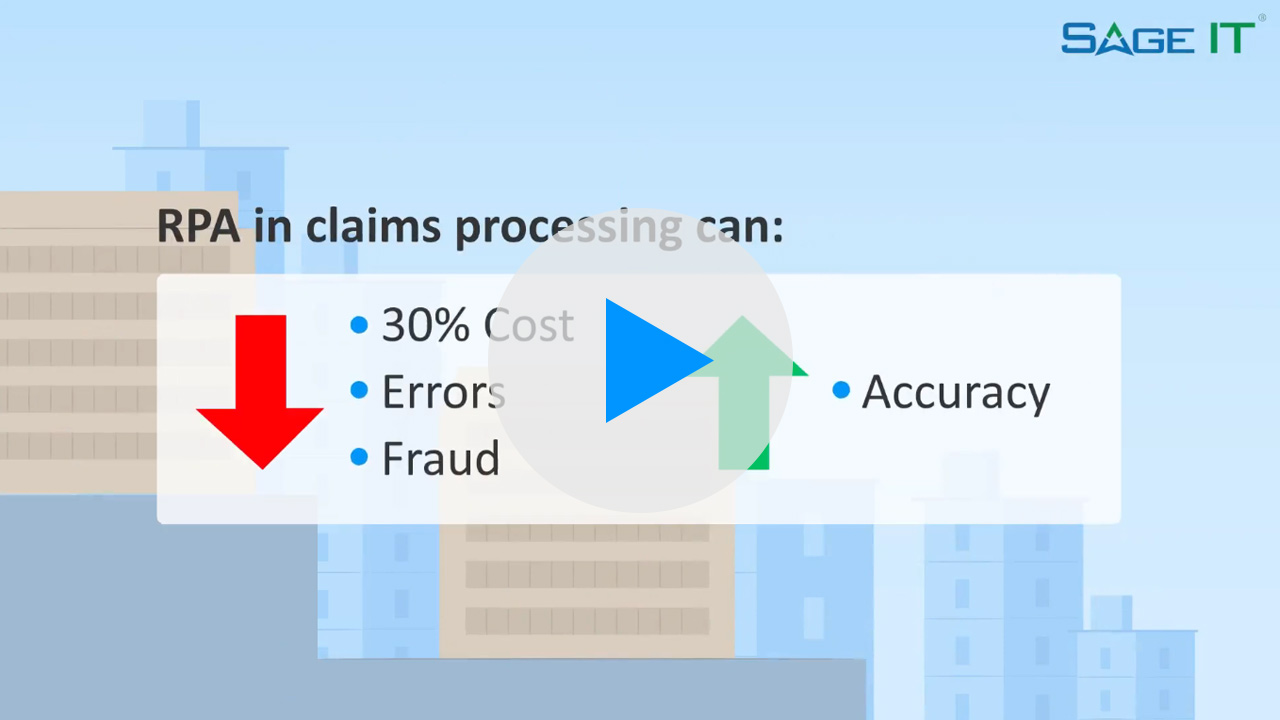
5. Supply chain – RPA determines that the part is not in stock and places an order for the part. Determined that standard shipping will not meet the timeline and requested expedited shipping.
6. Supply chain (alternate) – Instead RPA could search several vendors for the best price and delivery date.
7. Monitor shipping – daily, RPA checks shipping status to ensure timelines are being met.
8. Part arrival – once the part arrives, RPA puts the machines that need the part on the daily work list and assigns it to a tech.
9. Logging – once the part replacement is completed, RPA can update all the notes with data from Xen-Assist and send out a notification to stakeholders that repair/maintenance is completed.
10. Review – RPA can review the logs and determine that word was completed without issues.
11. Audit – RPA can be used to audit all the PMs
To know more about the different ways in which Sage IT can help you in your automation journey, visit: https://sageitinc.com/services/predic...